Key Takeaways
- China controls 90% of rare earth processing, leveraging decades of strategic policy and lax environmental standards .
- Heavy rare earths like terbium and dysprosium face near-total Chinese monopoly, crippling defense and green tech sectors .
- New export controls enacted in 2024 allow Beijing to restrict dual-use items, impacting semiconductors and AI technology .
- A Chinese Academy of Sciences study predicts China’s share of rare earth mining will drop to 28% by 2035 as global rivals emerge .
- U.S. ventures like NioCorp and Phoenix Tailings struggle against Chinese pricing power and investor skepticism .
Underground Vaults and Global Panic
Deep in a WWII-era vault near Frankfurt, Louis O’Connor guards ingots of terbium and dysprosium. Armed patrols circle thick concrete walls. Investors beg to buy his entire stock. China just tightened export controls on seven rare earth elements. O’Connor calls it a “tap system.” Beijing turns the flow on or off for political leverage. Foreign factories halted production lines weeks after China’s April 2025 licensing rule. Trade negotiations stalled. Rare earths became bullets in an economic war .
Stolen Knowledge and Cheap Acid
America unearthed rare earths first at Mountain Pass, California in 1949. Chinese delegations toured the site for decades. They took photos. They asked questions. They stole refining blueprints. Back home, hundreds of processing plants sprouted. State-subsidized electricity fueled refineries. Private mines competed viciously. They slashed prices. They poisoned villages. Southern China’s hills bled toxic waste. Workers poured hydrochloric acid into unlined pits. Rainstorms washed sludge into groundwater. Locals protested. Officials ignored them. Revenue trumped ruin .
The “Big Six” Monopoly
By 2011, Beijing declared war on its own rare earth chaos. Provincial agents dynamited illegal mines. Auditors seized contraband ore. Authorities merged surviving companies into six state-controlled giants. “One plus five,” they called it. A secret purge. Independent operators vanished. Prices homogenized. Competitive bidding died. The “Big Six” now dictate global supply. Traders like Frankfurt’s Jan Giese face rigid quotes. China shifted from export quotas—banned by the WTO in 2014—to corporate consolidation. Control without fingerprints .
Environmental Carnage
Jiangsu province, 2003. Investor Chris Ruffle smelled smoke. Thick plumes rose from a rare earth refinery. Tailings piled naked on the soil. No containment. Southern China’s “ion-adsorption clays” held precious heavy rare earths. Peasants mined hillsides with shovels. They doused dirt with sulfuric acid. Storms flushed poison into rivers. A 2012 state media investigation compared the trade to drug trafficking. “Two types of people deal rare earths: ex-cons and those who spring cons from jail,” it said. Death or profit. No middle ground .
China’s New Export Chokehold
Table: 2024 Dual-Use Export Controls
December 1, 2024. New dual-use regulations take force. MOFCOM consolidates control lists. Ten industry sectors. Five categories. Unified codes mirror the Wassenaar Arrangement. The rules demand end-user disclosures. They impose a “Watch List” for non-cooperative importers—China’s version of the U.S. “Unverified List.” General licenses require pristine compliance records. Foreign firms face re-export bans if their products contain Chinese tech. Third-party logistics providers must report suspicious shipments. Violators risk $500,000 fines. Extraterritorial reach mirrors U.S. sanctions. Tit-for-tat geopolitics .
Western Scramble and Capital Drought
Mark Smith sees empty investor desks. His phone stays silent. He ran Molycorp—America’s last major rare earth firm. It collapsed in 2015. Chinese price crashes buried it. Now Smith leads NioCorp in Nebraska. He begs for defense grants. Investors chase Amazon stock. Not mines. Processing rare earths demands specialized plants. It spews radioactive waste. Western regulations strangle startups. Phoenix Tailings reclaims mining waste in Massachusetts. CEO Nicholas Myers fought for years. China’s April 2025 export freeze changed everything. Automotive giants panicked. Funding arrived. His New Hampshire plant will soon cover half of U.S. defense magnet needs. Late urgency .
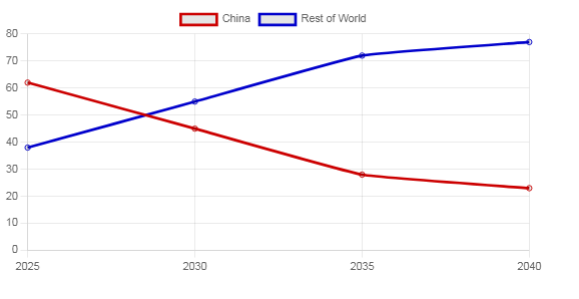
The 2035 Tipping Point
Graph: Projected Rare Earth Mining Share (%)
Chinese Academy of Sciences researchers published a forecast. China’s rare earth mining share will crater. 62% today. 28% by 2035. Greenland’s Kvanefjeld mine opens. South American projects accelerate. Africa extracts more ore. Heavy rare earth strongholds in Jiangxi face competition. China won’t disappear. Its refining grip stays ironclad. But raw ore dominance crumbles. The study calls it “fundamental shift.” Inevitable erosion .
Recycling, Substitution, and Other Miracles
Japan stockpiled neodymium after China’s 2010 embargo. It funded Australia’s Lynas Corporation. Dependence dropped 30%. The West lacks that discipline. Recycling rare earths remains sci-fi. Less than 1% recovery rate. Electric motors get shredded. Magnets landfill. Substitution efforts inch forward. Oak Ridge Labs tests iron-nitride compounds. Ceramic alternatives crack under stress. NioCorp’s Smith scoffs. “Defense systems need terbium. You can’t wish it into existence.” Nebraska mines might yield 20 tons yearly by 2029. China sells 200 tons now. The math stings .
Permanent War
China’s Politburo sees rare earths as artillery. It fires export curbs at Washington’s tariffs. MOFCOM’s “control list” aligns with the unreliable entities list. Blacklists multiply. Foreign companies face impossible choices. Obey U.S. sanctions? Violate China’s bans on cooperating with foreign regulators? Penalties hit $3 million. Nebraska’s dirt holds promise. Greenland’s mines creep forward. The CAS study whispers decline. But today, China’s fist stays tight. The vaults in Frankfurt stockpile panic .
FAQs
Q: Can the West compete with China in rare earth processing?
A: Not before 2030. China controls 90% of refining. U.S. facilities like MP Materials lack heavy rare earth capabilities .
Q: What makes heavy rare earths like dysprosium critical?
A: They prevent demagnetization in EV motors and precision missiles. China processes nearly 100% globally .
Q: How did China undercut Western rare earth producers?
A: State subsidies, low environmental enforcement, and predatory pricing collapsed rivals like Molycorp by 2015 .
Q: Are there non-Chinese sources for heavy rare earths?
A: Greenland’s Kvanefjeld project and NioCorp’s Nebraska site aim to produce them post-2028 .
Q: Do China’s 2024 export rules impact foreign companies?
A: Yes. Re-exports of items with Chinese tech face restrictions. Compliance risks global supply chains.




Comments
Post a Comment